INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 01

INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 02

INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 03
- Natural Language or NL refers to the common spoken or
written language spoken by humans. More info at
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_language
- Entity-Relational Language or ER refers to the language
used mainly represent databases. More info at
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Entity_relationship
- UML or Unified Modeling Language is a modeling language
used in software engineering to represent various
architectural elements of a system. More info at
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unified_Modeling_Language
- XML or eXtensible Markup Language is a language used to
capture data and metadata mainly from documents. More info
at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML
The main objective of a logic is to express, by means of a formal language, the knowledge about a certain phenomenon and encode with a precise set of rewriting rules (inference rules) the basic reasoning steps which are considered to be correct by everybody. A correct reasoning allows to show that a certain knowledge is a logical consequence of a given set of facts. Correct reasoning chains are constructed by concatenating applications of simple inference rules.
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 04
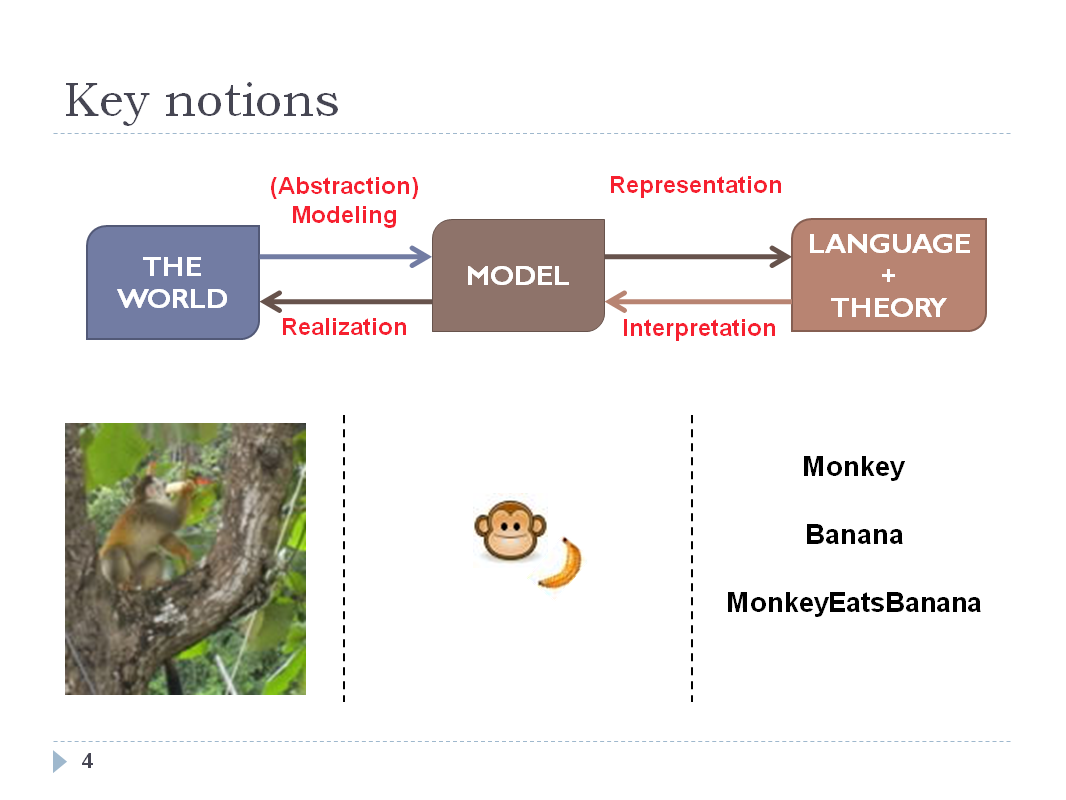
The top part of the slides shows three key stages and the
processes that are used to move between them. The bottom part
of the slides states the monkey example(that will be widely
used during the rest of the course):
- World: we have the photo of a monkey eating a banana on a
tree
- Model: stylized representation of the monkey (i.e. the
modeling simplified and filtered some elements from the
world).
- Language+Theory: the scene is reduced by three texts,
which are the name of the entities (Monkey and Banana) and
the description of the action (MonkeEatsBanana).
The following slides will have information on each of the key
notions (world, model and language+theory) presented in this
slide.
--
Actually, there is a semantic gap between the real world and the model. The gap is how to abstract the objects in real world to a mental model which can be entailed to theory and realized back to the real world.
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 05

INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 06

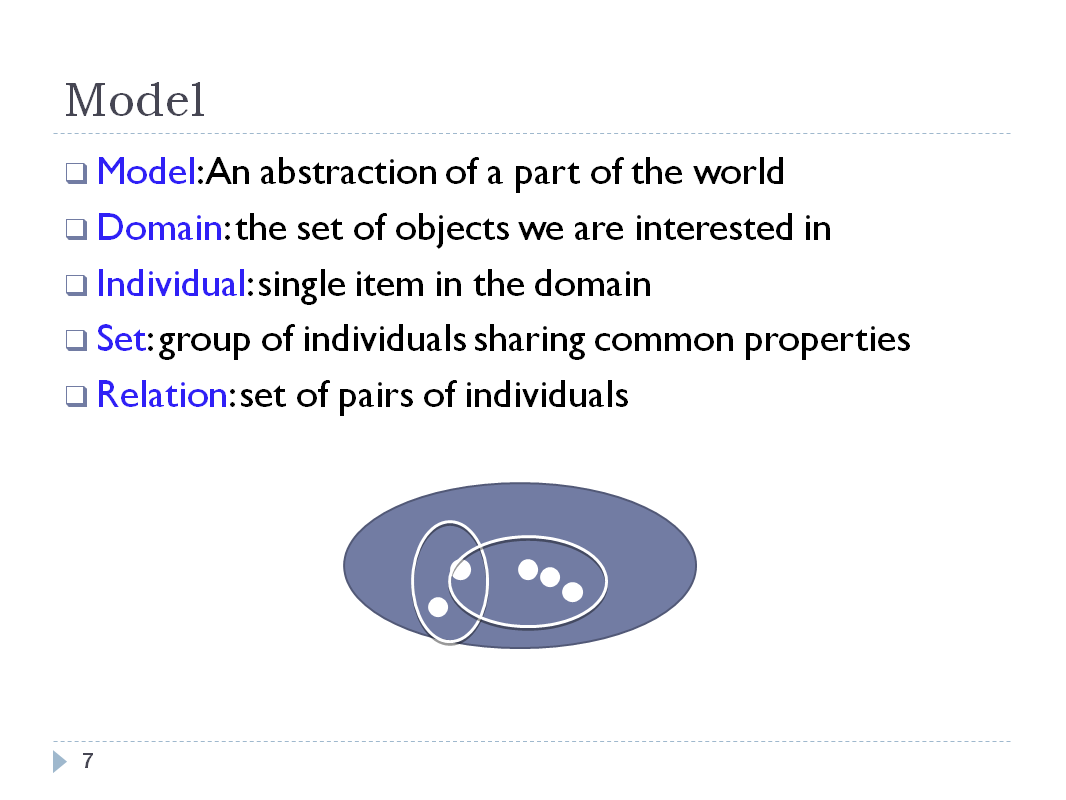
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 07
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 08
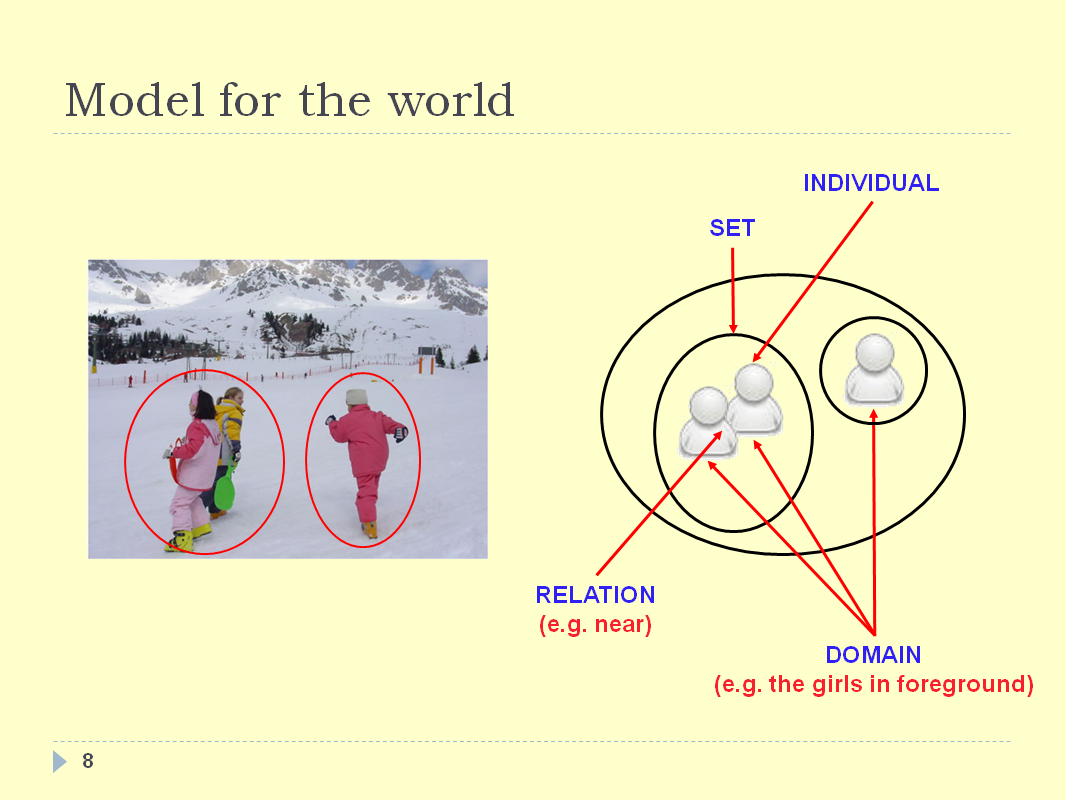
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 09

Short clarification about Logics (since there are going to be
used quite a lot in the following slides)
- PL or Propositional Logic is mainly used to derive
theorems from a series of formulas. Example: P -> Q
(and, or, then and not are some other relations available).
More information at
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Propositional_logic
- FOL or First Order Logic (also known as predicate logic),
uses quantifiers (like the “inverted A” which
means “for all” and the “inverted
E” which means “exists one”). More
information at
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/First-order_logic
- DL or Descriptive Logic: besides propositions (or
concepts as they are known, DL also introduces Individuals
and Roles. DL also introduces relationships like
“equivalent”, “defined to be
equal”, “is related”. More information at
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Description_logic
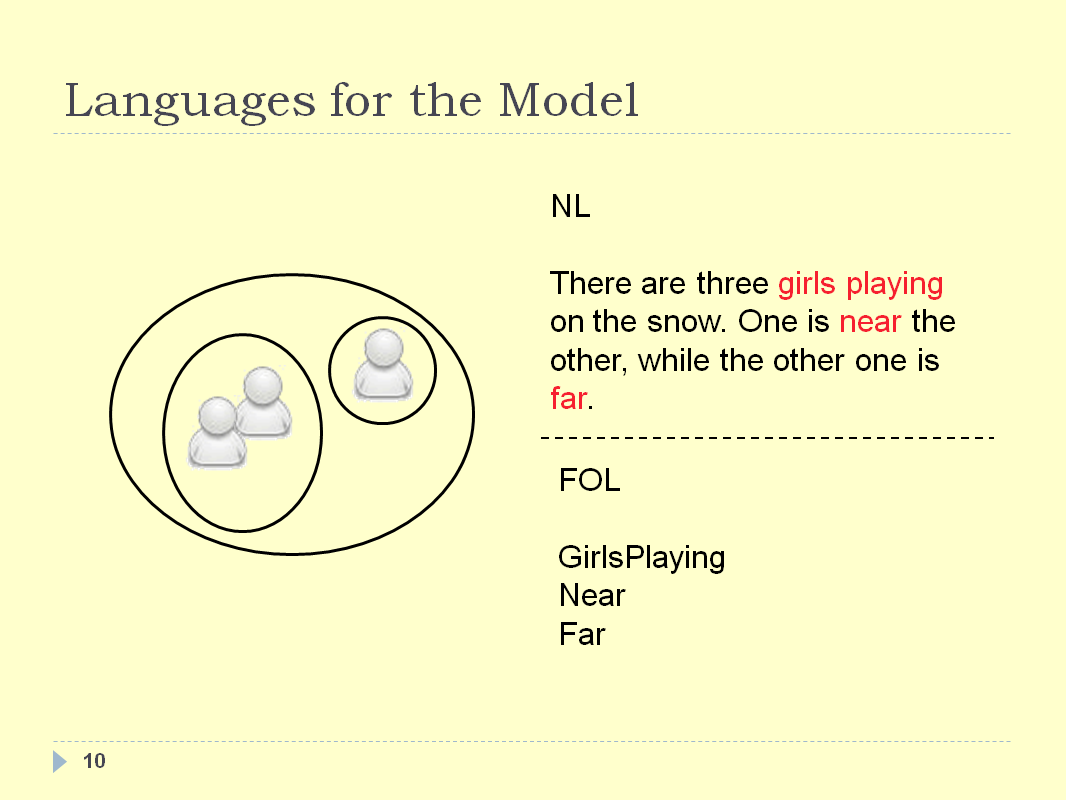
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 10
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 11

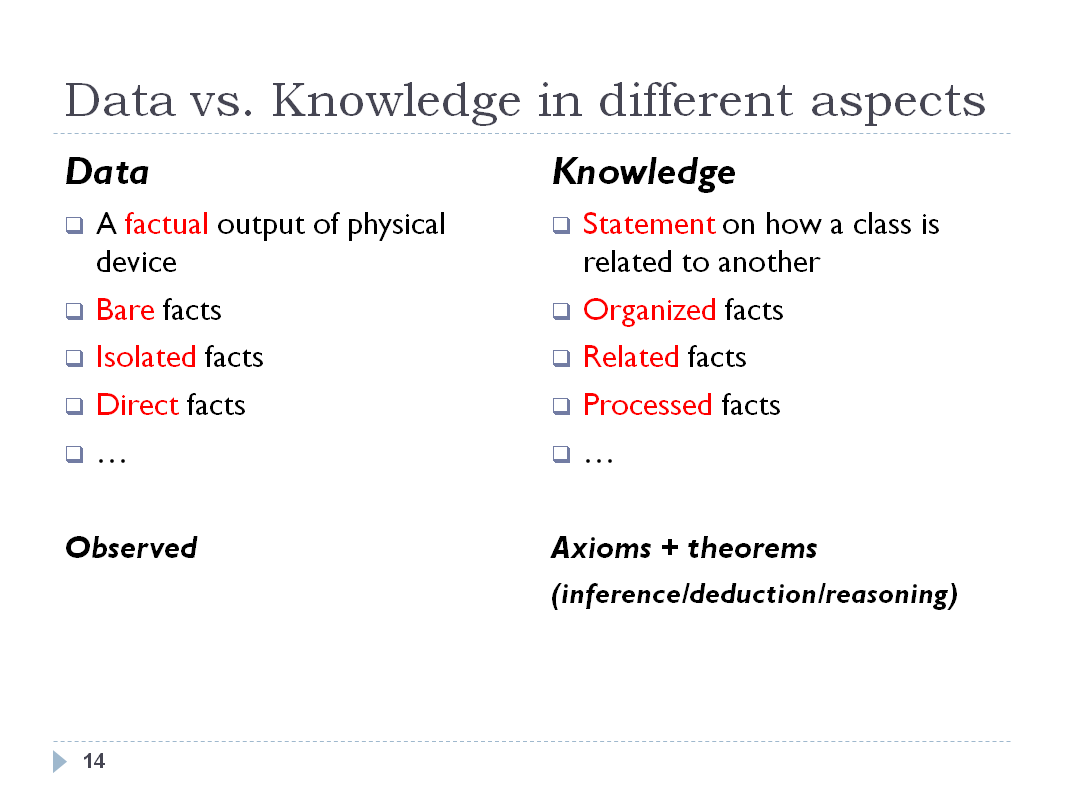
An important note is about the difference between data and
knowledge. Data can be thought as variables assuming different
values, let's take dw=7 just for example; we miss the
INFORMATION because no context is given. If I state that dw is
the total number of days in a week, I immediately get the
information that a week is composed by 7 days.
Essentially, knowledge is provided by a reasoning procedure
about data and information.
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 12
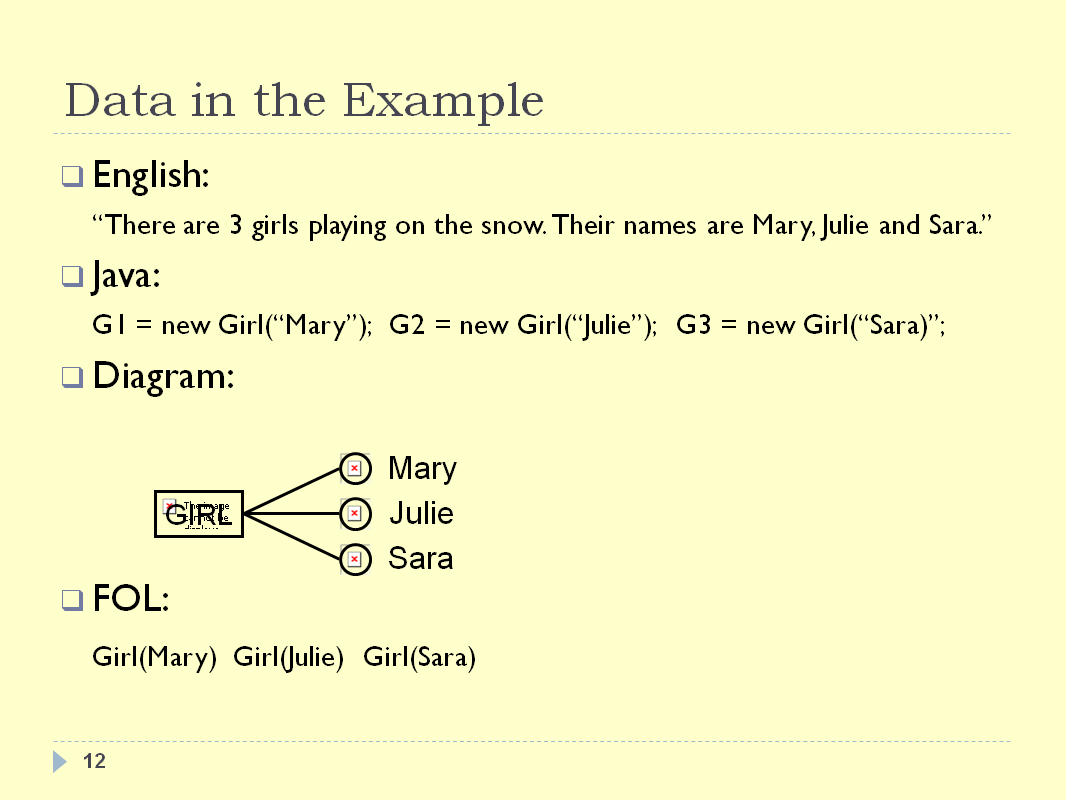
This slides gives an example across different languages and
representations:
- The English data has the most straight forward
description.
- In the Java description three “girl
variables” are defined and a string representing
their names is loaded into it.
- The diagram defines 3 circles representing the girls
(with her names) and connects them to a concept box
“GIRL”.
- In first order logic three propositions are created, each
stating that one of the names is a girl.
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 13
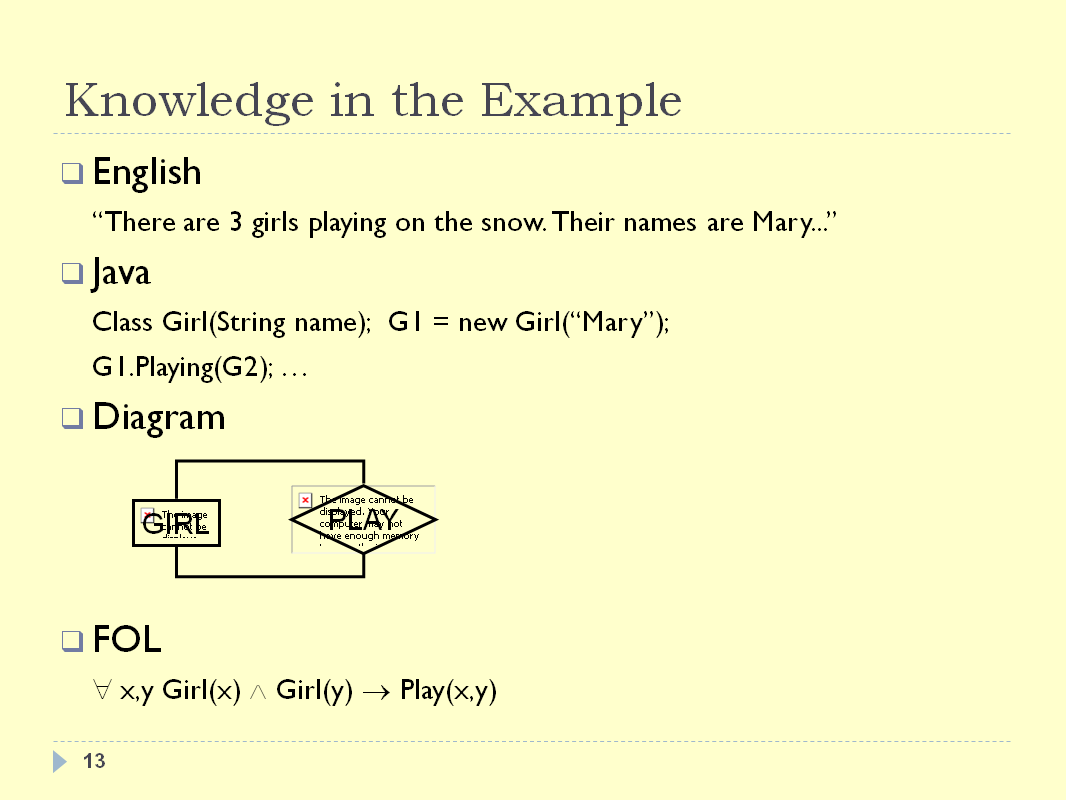
Now an action is added to the previous statement, this affects
the representation in the following manner:
- English: the sentence that describes the action was
simply appended at the beginning of the sentence.
- Java: the definition of girl was stream-lined by defining
a “Girl class”. Furthermore the attribute
“Playing” from the girl class is used to
indicate with who the current girl instance is playing.
- Diagram: a parallelogram with the word “PLAY”
was connected to “GIRL”, thus implying that
“all girls play”.
- The First-order logic represents the addition by saying
“For all x and y; if x is a girl and y is a girl,
then they play together”
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 14
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 15
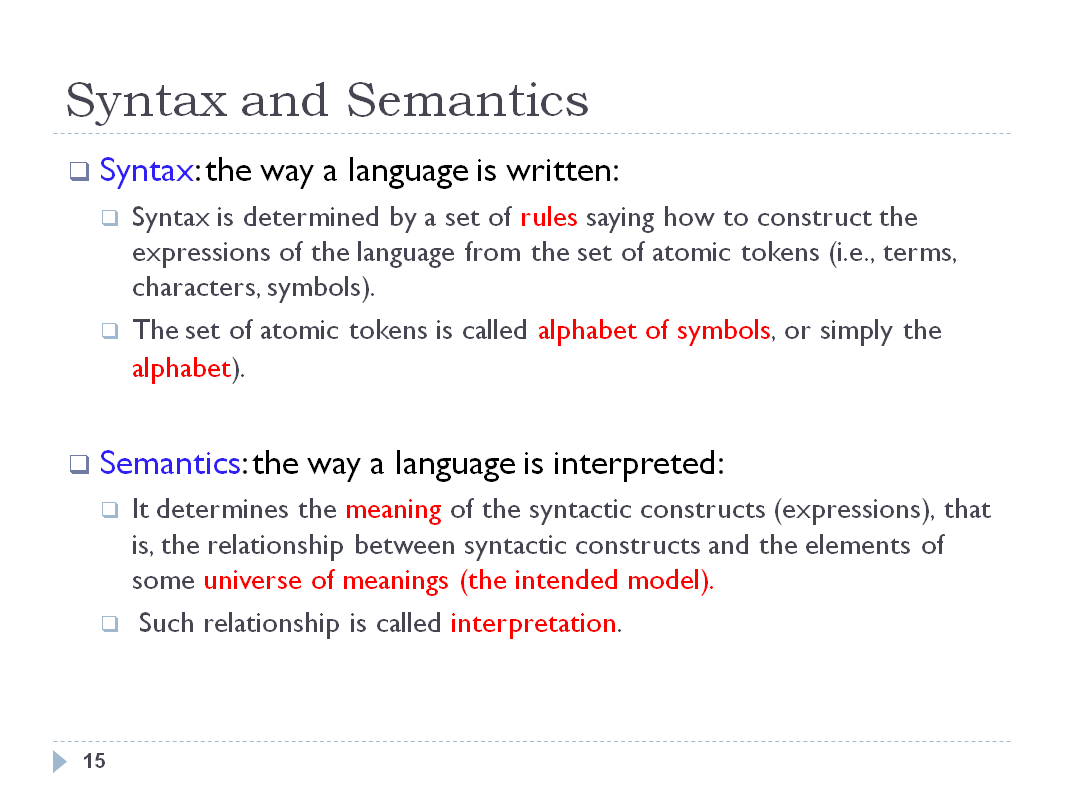
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 16
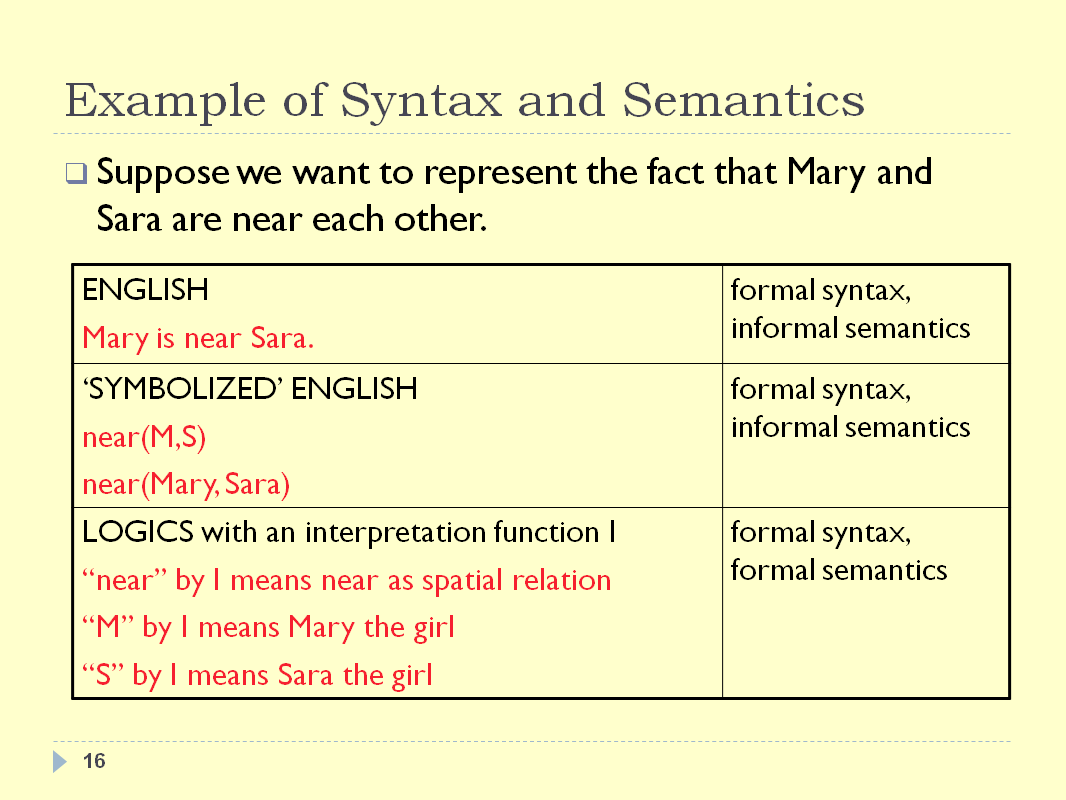
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 17
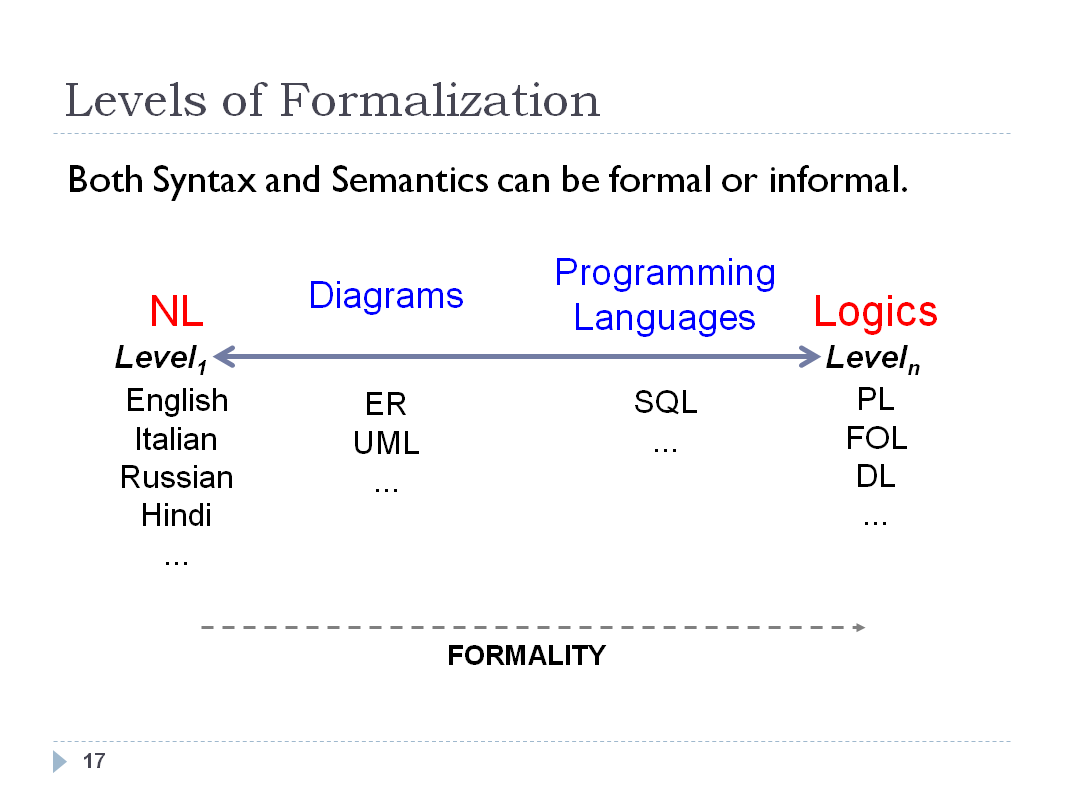
INTRODUCTION - SLIDE 18

|